Google has been making a big deal out of privacy lately, but Google+ just launched a slew of new features designed to make people easier to find.
I am particularly intrigued by the new Ripples feature, which allows you to see who has shared a post and track it as it gets shared by others. It is, in fact, like watching a ripple.
Ripples strikes me as much more of a feature for marketers than for consumers. I suppose Google+ wants to attract power users who typically have more of a marketing mindset than the average Joe.
So of course the first thing I thought of was that Ripples would be an excellent tool to find local influencers on Google Plus. Here’s how:
(Warning: The techniques described below are merely for educational purposes. I take no responsibility for the potential spam and privacy issues Google has unleashed here.)
1. First Find Google+ Users In Your Target Location
I am sure Google+ will eventually have some nifty ways for you to find people near you who share similar interests, but let’s say you wanted to find those people today. Perhaps you want to engage with them about subjects you share in common.
Maybe you’re a vegan restaurant in the Bay Area and you want to build a network of local vegans to share recipes with and perhaps at some point get them to promote your restaurant. Well there’s an app for that — a search app that is, called Google.
Go to Google and do the following search:
This query shows you URLs of Google+ members who use the word “vegan” and whose profiles show that they live in the Bay Area. Depending on the query, you may need to play around with this a bit by adding additional filters. For example, if you were looking for people in Brooklyn but didn’t want to find people named “Brooklyn,” you would add “-intitle:Brooklyn”.
Here are the top results of my Bay Area vegan query:

2. Find People Who Are Interested In What You Have To Say
Google gave 2,740 results for this query, which means that you now can find several hundred people who might be interested in your vegan vittles. You could click on each of their profiles and figure out which ones seem interesting and willing to engage, but first:
3. Find The Most Active/Influential Ones
Go back to Google and do the following query:
This query, in theory, will show you all of the posts for a particular member — in this case, me. As you can see, I have made 191 posts thus far (nothing about vegans, though):

If you want to see if the person has been active recently, click on the “Show Search Tools” link at the bottom of the left-hand navigation on the Google SERP:
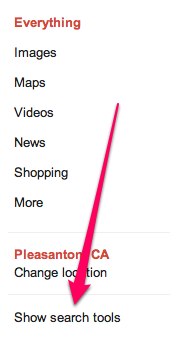
Set the filter to “Past 24 hours” or “Past week” or a custom range to see how active the person is.
Once you have found the right people, it’s time to check out some Google+ Ripple action. Review the posts by the member that contain the keyword you are interested in by doing the following query in Google Plus:
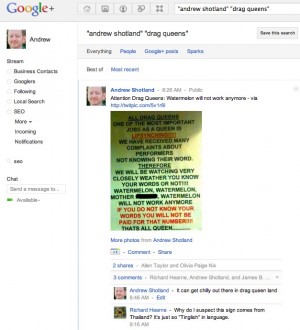
When you have found a post that looks relevant to your subject click on the “View Ripples” link on the drop-down menu in the upper right-hand corner of the post:

Now, you can see who else has shared this post:

This data shows you how influential the person is, how popular the post is and who else is interested in the subject. By examining this data for each member, you can start to figure out who is most influential about your subject matter in your area.
Once you have built the list, then it’s up to you to figure out how to engage with them in a way that will be mutually beneficial and help get your message out.
Now it goes without saying, but I’ll say it anyhow: These techniques are only valuable if you can convince people to invest their attention in you.
And there are no magic queries in Google that can do that for you.
Opinions expressed in the article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land.
Related Topics: Google: Social Search | Locals Only




